Muscular Dystrophy
What Is Muscular Dystrophy? Muscular dystrophy (MD) is a that weakens the muscles that help the body move. Free ats resume scanner. People with MD have incorrect or missing information in their genes, which prevents them from making the proteins they need for healthy. Because MD is genetic, people are born with the problem — it's not contagious and you can't catch it from someone who has it. MD weakens muscles over time, so children, teens, and adults who have the disease can gradually lose the ability to do the things most people take for granted, like walking or sitting up. Someone with MD might start having muscle problems as a baby or the symptoms might start later. Some people even develop MD as adults.
Muscular Dystrophy Treatment
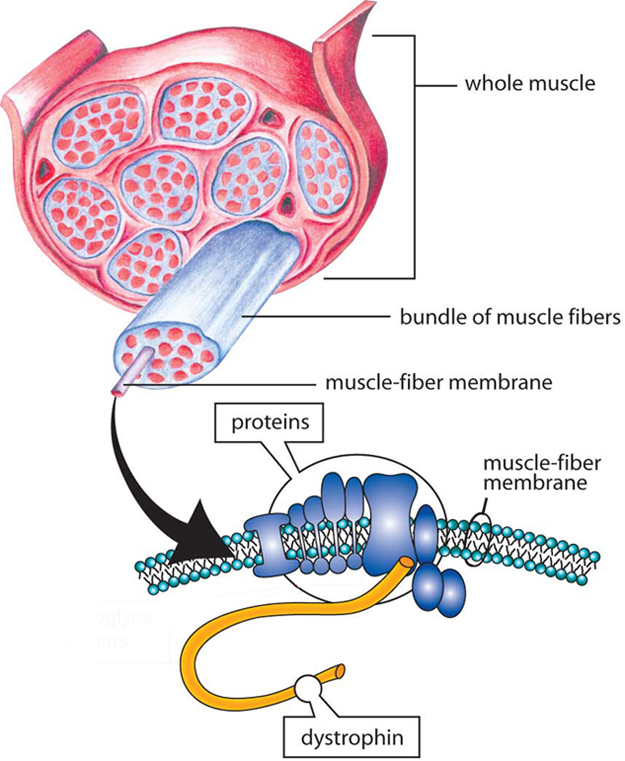
Several major forms of muscular dystrophy can affect teens, each of which weakens different muscle groups in various ways: • Duchenne (pronounced: due-SHEN) muscular dystrophy (DMD), the most common type of the disease, is caused by a problem with the gene that makes a protein called dystrophin (pronounced: dis-TROH-fin). This protein helps muscle cells keep their shape and strength. Free chatroulette token codes for mac. Without it, muscles break down and a person gradually becomes weaker. DMD affects boys. Symptoms usually start between ages 2 and 6. By age 10 or 12, kids with DMD often need to use a wheelchair. The heart may also be affected, and people with DMD need to be followed closely by a lung and heart specialist.
Muscular Dystrophy Life Expectancy
Muscular dystrophy is a hereditary medical condition that greatly affects the muscles of the body and causes progressive weakness. Lightroom alternatives for mac. Fontgenius mac. While there are fewer than 200,000 cases in the United States, as of right now, there is no cure. Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe type of muscular dystrophy. The symptom of muscle weakness usually begins around the age of four in boys and worsens quickly.